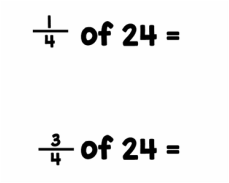
As we come to the end of the year, I've been thinking about how I've used number talks in my class this year. As I moved from Primary 1 (kindergarten) last year to Primary 3 (2nd grade) this year, it has been a bit of a challenge at times. Why? Because my understanding of mathematics is largely procedural. I can look at a problem and follow the algorithm I was taught years ago and get the right answer. BUT - I often have only a vague understanding of why the algorithm works. And I definitely struggle to 'think outside the box' and solve problems in ways I wasn't taught.
This year, I've found that I've needed to work hard (and pull out concrete materials to aid my own understanding of why a given strategy works!) to really understand what is happening when I use the multiplication algorithm, for example. Or how I can split numbers apart and combine them in different ways to mentally solve problems that the 2nd grade me would have definitely used paper, pencil and algorithm for.
I think this is the main reason why number talks can be daunting for teachers at first - we are asking our kids to reason about mathematics that we might find just a little bit tricky ourselves (luckily, I've only been teaching Primary 3!). And what if the kids come up with a strategy that we can't follow, or that we can't make clear to the rest of the class? I benefited, I think, from starting the Number Talk process in kindergarten, so the different strategies I was getting my head around were simple.
But when you teach this way, you really open up an exciting mathematical world for your pupils. As the year has progressed, I've often found myself thinking that some of my class have a much better intuitive grasp of mathematical fundamentals than I have (oops). They can reason with numbers in a way that often just never occur to me.
Take as an example, the 2 fraction equations given above. I put the first equation to my class yesterday morning, and many of the kids were able to tell me that the answer was '6'. To help, I put up 24 different magnetic cubes, and we split them up into our 4 groups, so we could all see the 6 cubes in each group.
Then we moved to the second equation. Again, a reasonable number of children could tell me that the answer was 18 (although this concept is definitely trickier for a lot of them!). But when I asked one little boy to defend his answer, this is what he told me:
I knew that 1/4 of 24 was 6, and I had 3/4 left, so I took 1/4 (which is 6 cubes) away from 24 to get 18.
Oh, My. Goodness. Of course - how simple. But it never in a million years would have occurred to me.
Implementing number talks can be tricky. And you will definitely stretch your own understanding of mathematical processes as you implement them. But the rewards for your pupils are amazing, so I would really encourage you to give it a try. Start simple - even if you are teaching an older class, if they aren't familiar with number talks and having to explain their mathematical thinking, they will thank you (and you will thank yourself!) for starting slowly. But give it a try - you won't regret it.
This year, I've found that I've needed to work hard (and pull out concrete materials to aid my own understanding of why a given strategy works!) to really understand what is happening when I use the multiplication algorithm, for example. Or how I can split numbers apart and combine them in different ways to mentally solve problems that the 2nd grade me would have definitely used paper, pencil and algorithm for.
I think this is the main reason why number talks can be daunting for teachers at first - we are asking our kids to reason about mathematics that we might find just a little bit tricky ourselves (luckily, I've only been teaching Primary 3!). And what if the kids come up with a strategy that we can't follow, or that we can't make clear to the rest of the class? I benefited, I think, from starting the Number Talk process in kindergarten, so the different strategies I was getting my head around were simple.
But when you teach this way, you really open up an exciting mathematical world for your pupils. As the year has progressed, I've often found myself thinking that some of my class have a much better intuitive grasp of mathematical fundamentals than I have (oops). They can reason with numbers in a way that often just never occur to me.
Take as an example, the 2 fraction equations given above. I put the first equation to my class yesterday morning, and many of the kids were able to tell me that the answer was '6'. To help, I put up 24 different magnetic cubes, and we split them up into our 4 groups, so we could all see the 6 cubes in each group.
Then we moved to the second equation. Again, a reasonable number of children could tell me that the answer was 18 (although this concept is definitely trickier for a lot of them!). But when I asked one little boy to defend his answer, this is what he told me:
I knew that 1/4 of 24 was 6, and I had 3/4 left, so I took 1/4 (which is 6 cubes) away from 24 to get 18.
Oh, My. Goodness. Of course - how simple. But it never in a million years would have occurred to me.
Implementing number talks can be tricky. And you will definitely stretch your own understanding of mathematical processes as you implement them. But the rewards for your pupils are amazing, so I would really encourage you to give it a try. Start simple - even if you are teaching an older class, if they aren't familiar with number talks and having to explain their mathematical thinking, they will thank you (and you will thank yourself!) for starting slowly. But give it a try - you won't regret it.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed